Why should you care about prebiotics and postbiotics?
Why should you care about prebiotics and postbiotics?
By embracing prebiotics and postbiotics, you’re helping your gut help itself. Prebiotics and postbiotics represent deep nourishment that satisfies and balances the body from the inside out. Everyone has a health journey, and it always starts in the gut.

Prebiotics feed the good bacteria in our gut. Prebiotics come from fiber in vegetables, or even polyphenols (the plant nutrients that turn fruits and vegetables bright colors) found in foods like olive oil, green tea, cranberry, pomegranate, grape seed and more. Postbiotics are the byproducts that come from good gut bacteria fermenting undigested fiber, resistant starches and polyphenols in your gut,. The most important and foundational postbiotic is BUTYRATE (i.e. CoreBiome®). Butyrate is arguably the most important nutrient to humans’ health—-period.
The difference between prebiotics and postbiotics goes a lot deeper than the above. Below is an oversimplification, but the basics are as follows:
- You eat fibrous plants like broccoli and the undigested part is fermented in the colon by good bacteria
2. The good bacteria produce the postbiotic—butyrate—in this fermentation process.
3. The fermented butyrate is what makes up your gut barrier protector, protecting you from pathogenic bacteria entering your blood stream and causing widespread inflammation
4. The fermentation byproducts (such as butyrate) are what make up postbiotics.
In this article, we’ll explain the difference between prebiotics and postbiotics in an easy-to-digest way (we love puns!), and why they matter to your health. Want to get to a scholarly article on this topic? Learn More.
Butyrate 101
First, we have to talk about butyrate, your #1 gut barrier protector. Butyrate is a postbiotic and part of three compounds called short chain fatty acids (SCFAs, if you’re in the know!). With undigested fiber and resistant starches, the good bacteria in our colon ferment and produce short-chain fatty acids One specific type of SCFA is butyrate. Butyrate is particularly important because it’s responsible for the lining of your intestinal wall. Without this lining, bad bacteria have access to your internal organs and blood stream. Can you imagine bad bacteria circulating throughout your body via your blood? It sounds like a bad dream, right?
But that’s exactly what’s happening with low butyrate production and leaky gut!
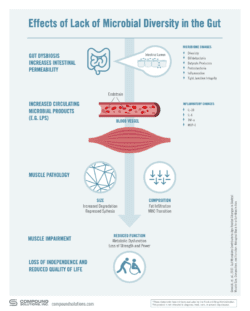
After reading the above, you’ll likely be unsurprised to hear more than 70% of our immune cells reside in the gut. That’s right; your immunity isn’t dependent on your vitamin C and elderberry gummy. The status of your immunity is a function of the integrity of your gut lining.
Without an optimized immune system, we’re susceptible to various infections, viruses and diseases.
Takeaway here: Prebiotics are important for the production of butyrate (postbiotic) in the body. The more prebiotics you get by eating natural plant fiber, the more you benefit from your body producing postbiotics. This matters for overall digestion and regularity, as well as brain, skin and immunity Note: To supercharge your gut health and quickly enhance your gut barrier, supplementing directly with CoreBiome® is key. CoreBiome is a patented, bioavailable source of butyrate.
Are Postbiotics important?
Yes, postbiotics are the icing on the carrot cake!
Postbiotics are not an after-thought or something to casually consider in one’s quest for real gut harmony. In fact, we believe that the benefits are of primary importance even though the benefits quite literally come out in the end.
The Difference between prebiotics and postbiotics

The difference between prebiotics and postbiotics is that, simply put, prebiotics are the fibrous foods we eat. They kickstart the butyrate production process in the colon. Postbiotics are the “exhaust “or byproducts of the digestive process. Butyrate produced from this process has arguably the single greatest impact on your health. Nothing is more important. The benefits to healthy butyrate levels include optimized gut, brain, heart, skin and immune health. Postbiotics are just as crucial to the gut health journey as prebiotics.
What are Prebiotics?:
Prebiotics are mainly soluble fibers, but also include polyphenols like green tea, cranberry, grape seed and pomegranate. The fiber and polyphenols provide food for your gut microbiota. This helps good bacteria grow and outcompete any bad bacteria for colonization in the gut.
.
What are Postbiotics?:
Postbiotics are the end-products of the fermentation process in the colon.When good bacteria in the colon break down prebiotic fibers, this is the fermentation process. Butyrate is produced and your gut barrier is enhanced.
So, why should you care about prebiotics and postbiotics? Because they are THE foundation of your health. Without a foundation, you can’t build a healthy house.
Where can you find postbiotics?
Nothing is better than real, whole foods. Fibrous vegetables and fruits are where we should all be getting our fiber (to be used as prebiotics). The reality is that 95% of Americans are not getting enough fiber. If we’re not getting enough fiber, then we have butyrate deficiency and a leaky gut epidemic. This is where supplements come in. You can find Corebiome® in a variety of functional supplements on the market now.
So, while eating a balanced diet with fibrous vegetables, integrate CoreBiome® to supercharge your results.
Read this if you want to learn more about gut health and why postbiotics matter.
Want to formulate for postbiotics and have questions? Contact us!





